Hierarchy.ToLocal
static Vec3 ToLocal(Vec3 worldPoint)
Converts a world space point into the local space of the current Hierarchy stack!
| Vec3 worldPoint | A point in world space. |
| RETURNS: Vec3 | The provided point now in local hierarchy space! |
static Quat ToLocal(Quat worldOrientation)
Converts a world space rotation into the local space of the current Hierarchy stack!
| Quat worldOrientation | A rotation in world space. |
| RETURNS: Quat | The provided rotation now in local hierarchy space! |
static Pose ToLocal(Pose worldPose)
Converts a world pose relative to the current hierarchy stack into local space!
| Pose worldPose | A pose in world space. |
| RETURNS: Pose | The provided pose now in local hierarchy space! |
static Ray ToLocal(Ray worldRay)
Converts a world ray relative to the current hierarchy stack into local space!
| Ray worldRay | A ray in world space. |
| RETURNS: Ray | The provided ray now in local hierarchy space! |
Examples
Spaces and Intersections
One tricky thing you need to keep in mind when working with
different spaces like the ones created with Hierarchy is that any
values you use for math need to be in the same space! I like to
explicitly label my variables with the space they’re in anytime I’m
working with anything even a little complicated!
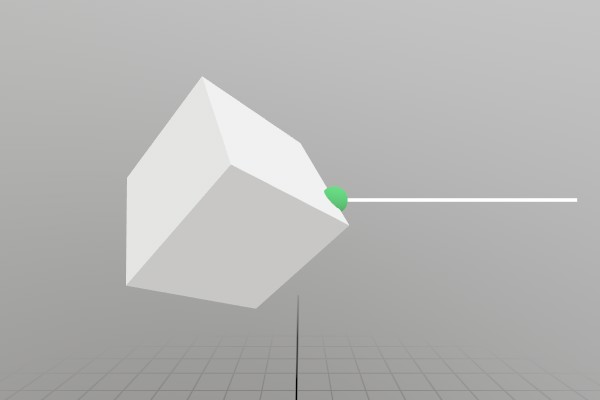
Here’s an example of intersecting a ray with some content that
exists inside of a Hierarchy stack. You always need to transform
your data into Mesh or Model space in order to do an
Intersect, but the Hierarchy here adds a bit of extra
complexity to the problem!
// It can often be helpful to consider if you're making a function
// "Hierarchy aware", meaning that it will still work properly if the
// code _already_ exists within a transformed hierarchy! Here we're
// using `Hierarchy.ToWorld` to ensure our intersection ray is
// _for sure_ in World Space.
Ray parentSpaceRay = new Ray(V.XYZ(0.5f, 4, -0.5f), V.XYZ(-1, 0, 0));
Ray worldSpaceRay = Hierarchy.ToWorld(parentSpaceRay);
Lines.Add(parentSpaceRay, 0.5f, Color.White, 0.005f);
// Sometimes it can help with clarity to add scope brackets to show
// how the hierarchy is affecting the code!
Hierarchy.Push(Matrix.T(0, 4, -0.5f));
{
Matrix localTransform = Matrix.TRS(Vec3.Zero, Quat.FromAngles(20, 135, 45), 0.2f);
Mesh.Cube.Draw(Material.Default, localTransform);
// Mesh intersection _must_ be done in Mesh space, since that's
// the space the Vertex data is in. So we need to convert our
// intersection ray all the way from world space to mesh space here
// before calling `Intersect`!
Ray localSpaceRay = Hierarchy.ToLocal(worldSpaceRay);
Ray meshSpaceRay = localTransform.Inverse.Transform(localSpaceRay);
if (meshSpaceRay.Intersect(Mesh.Cube, out Ray meshSpaceAt))
{
// Similarly, the intersection point needs to be transformed
// from Mesh space back into our local space before drawing it.
Ray localAt = localTransform.Transform(meshSpaceAt);
Mesh.Sphere.Draw(Material.Default, Matrix.TS(localAt.position, 0.04f), Color.HSV(0.36f, .8f, .8f));
}
}
Hierarchy.Pop();
Found an issue with these docs, or have some additional questions? Create an Issue on Github!
